CRFC BLOGS
LATEST BLOGS & NEWSLETTERS
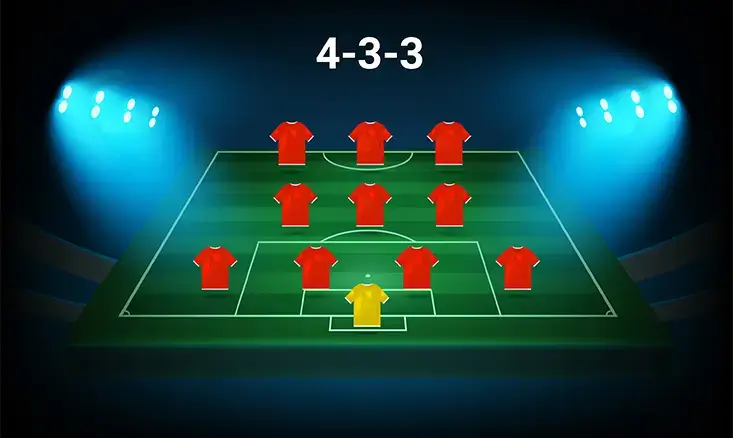
Comprehensive Guide to Youth Soccer 4-3-3 Formation
The 4-3-3 formation is widely regarded as one of the most effective setups in modern soccer. It’s a formation that balances defense, midfield control, and attack, making it particularly well-suited for youth soccer teams. By using the 4-3-3 formation, young players can develop crucial skills that will serve them well as they progress in their soccer careers. In this detailed guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about the youth soccer 4-3-3 formation, from understanding its structure to mastering the advanced tactics that can make your team stand out.
The Youth Soccer 4-3-3 Formation Structure and Positions
At its core, the 4-3-3 formation is built around a simple yet effective structure. The team is organized into four defenders, three midfielders, and three forwards. Each group of players has specific roles and responsibilities, which, when executed well, create a strong and cohesive team.
Defensive Line
- Center-Backs: The center-backs are the heart of the defense. Positioned at the center of the backline, these two players are responsible for marking the opposition’s forwards, intercepting passes, and clearing the ball from dangerous areas. They need to communicate effectively with each other and with the goalkeeper to maintain a solid defensive line.
- Full-Backs: The full-backs play on the left and right sides of the defense. Their role is twofold: defensively, they must track the opposing wingers and prevent crosses into the box. Offensively, they are expected to support the attack by overlapping with their wingers, providing width, and delivering crosses. This dual responsibility requires full-backs to have high stamina and tactical awareness.
Midfield Trio
- Holding Midfielder: The holding midfielder is a critical player in the 4-3-3 formation. This player acts as a shield for the defense, breaking up opposition attacks before they reach the backline. The holding midfielder also plays a key role in initiating attacks by distributing the ball to more advanced teammates. This position requires a player with strong defensive skills, good vision, and the ability to read the game.
- Central/Attacking Midfielders: The other two midfielders in the 4-3-3 formation are typically more attack-minded. The first midfielder contributes defensively and offensively. The second player is responsible for linking the midfield with the forwards, creating goal-scoring opportunities, and sometimes taking on the role of a secondary striker. Both positions require players who are comfortable on the ball, can make quick decisions, and have the stamina to cover a lot of ground.
Attacking Trio
- Central Striker: The central striker is the main goal-scorer of the team. Positioned at the top of the formation, this player’s primary job is to finish off attacks, whether by shooting directly at the goal or by setting up teammates. The striker needs to be strong enough to hold up the ball under pressure from defenders and skilled enough to finish with precision. In youth soccer, developing a striker who can play with their back to goal and involve others in the play is crucial.
- Wingers: The wingers in a 4-3-3 formation are key to creating width in the attack. Positioned on the left and right flanks, these players must be quick, agile, and comfortable taking on defenders one-on-one. Their primary roles include delivering crosses into the box, cutting inside to take shots, and stretching the opposition’s defense. Wingers must also be prepared to track back and assist in defense when necessary, making this a demanding but vital role in the formation.
Attacking in a Youth Soccer 4-3-3 Formation
The 4-3-3 formation is renowned for its attacking potential. With three dedicated forwards, it offers a constant threat to the opposition, especially when supported by attacking midfielders and overlapping full-backs.
Role of the Wingers
Wingers are the most critical players in the attacking phase of a 4-3-3 formation. Their role is to stay wide, stretching the defense and creating space for other attackers. By doing so, they can either take on defenders directly, cut inside to shoot, or deliver accurate crosses into the box. In youth soccer, developing wingers who are confident in taking on opponents and making quick decisions in the final third can make a significant difference in the team’s attacking effectiveness.
Central Striker’s Role
The central striker is the focal point of the team’s attack. This player must be adept at finishing, whether from crosses, through balls, or taking on defenders one-on-one. However, the striker’s role is not just about scoring goals. In a 4-3-3 formation, the striker is also expected to hold up the ball, allowing time for the wingers and midfielders to join the attack. This requires strength, good ball control, and an understanding of when to pass and when to shoot.
Midfield Support
The midfielders are crucial in supporting the attack. They must be prepared to push forward, make late runs into the box, and link up with the forwards. Their ability to maintain possession, distribute the ball effectively, and take shots from outside the box adds a layer of threat to the team’s attacking play. In youth soccer, encouraging midfielders to develop their attacking instincts while maintaining their defensive responsibilities is essential.
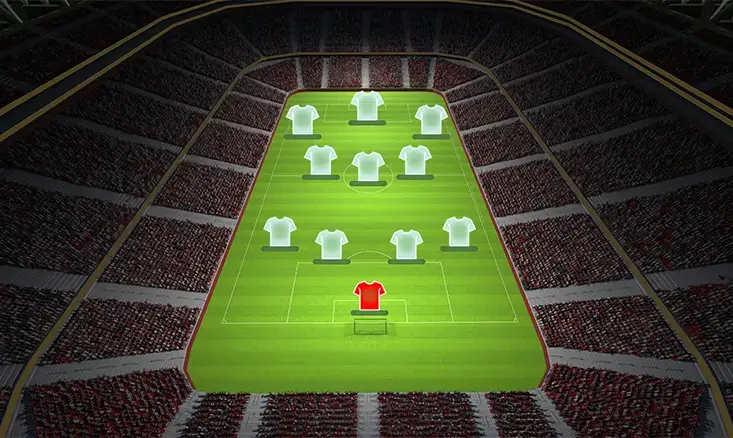

Defensive Considerations in a Youth Soccer 4-3-3 Formation
While the 4-3-3 formation is known for its attacking prowess, it’s equally important to maintain a strong defensive structure. A well-organized defense can prevent the opposition from exploiting the spaces that naturally open up when playing with three forwards.
Role of the Holding Midfielder
The holding midfielder is the foundation of the team’s defense in a 4-3-3 formation. This player’s primary responsibility is to protect the backline by intercepting passes, winning tackles, and breaking up opposition attacks. The holding midfielder also plays a vital role in transitioning from defense to attack, often acting as the link between the defenders and the more advanced midfielders. In youth soccer, developing a holding midfielder who understands positioning and can read the game well is crucial for maintaining defensive stability.
Full-Backs’ Responsibilities
Full-backs in a 4-3-3 formation have a demanding role. They must balance their defensive duties with the need to support the attack. When going forward, full-backs provide width and can deliver crosses into the box. However, they must also be aware of the space they leave behind, as opposition wingers can exploit this if the full-backs are caught out of position. Good communication with the center-backs and holding midfielder is essential to ensure the team is not vulnerable to counter-attacks.
Weaknesses of the Soccer 4-3-3 Formation
No formation is without its weaknesses, and the 4-3-3 is no exception. Understanding these potential pitfalls is key to mitigating them during games.
Susceptibility to Counter-Attacks
One of the most significant weaknesses of the 4-3-3 formation is its vulnerability to counter-attacks. With three forwards committed to the attack, the team can be exposed if possession is lost and the opposition quickly transitions to attack. This is especially true if the midfielders and full-backs are caught out of position. To counter this, teams must maintain discipline, with the holding midfielder staying back to cover, and full-backs being cautious about when to push forward.
Potential Gaps in Defense
Another challenge of the 4-3-3 formation is the potential for gaps to appear in the wide areas, especially if the wingers do not track back to help the full-backs. Opponents with fast wingers or overlapping full-backs can exploit these spaces, putting pressure on the defense. Drills that focus on defensive transitions and maintaining team shape can help young players develop the discipline needed to minimize these gaps and maintain a solid defensive unit.
Counter-Attacking and Holding Play in 4-3-3
Youth Soccer 4-3-3 Counter
Despite its attacking focus, the soccer 4-3-3 formation can be highly effective for counter-attacking. With three forwards positioned high up the field, the team is well-placed to exploit any opportunities that arise from turnovers. To execute a successful counter-attack, players must move the ball forward quickly, with the midfielders supporting the forwards to create overloads against the opposition defense. In youth soccer, training players to recognize counter-attacking opportunities and make quick, decisive passes is key to maximizing this aspect of the game.
Holding Play
In certain situations, particularly when protecting a lead, it’s important for the team to maintain possession and control the tempo of the game. The 4-3-3 formation allows for effective holding play, as the team can circulate the ball among the midfielders and defenders, waiting for the right moment to launch an attack. This approach requires patience, good passing skills, and a collective understanding of when to slow down the game. Coaches should incorporate drills that focus on ball retention and controlled passing into their training sessions to help young players develop these skills.
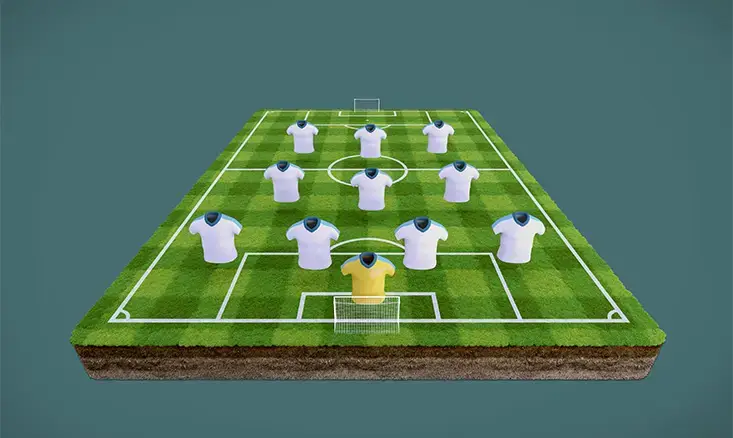

Youth Soccer 4-3-3 Formation Training Drills
Effective training is essential for mastering the 4-3-3 formation. Coaches should design drills that not only improve individual skills but also enhance the team’s overall understanding of how to play within this formation.
Positional Drills
Positional drills are crucial for helping players understand their roles within the 4-3-3 formation. These drills should focus on maintaining team shape, positioning, and movement off the ball. For example, coaches can set up exercises where players must keep their formation while moving the ball from defense to attack, ensuring they stay in their designated zones. This reinforces the importance of discipline and understanding one’s role within the team.
Attacking Drills
Coaches should emphasize drills that create and exploit space to sharpen the team’s attacking capabilities. Small-sided games that mimic match situations are particularly effective, as they force players to make quick decisions, move off the ball, and combine with teammates to break down a defense. Additionally, practicing finishing from different angles and distances can help forwards develop the composure needed to score goals in competitive matches.
Defensive Drills
Defensive drills are just as important as attacking ones. These soccer defensive exercises should focus on communication, marking, and coordination among defenders and midfielders. For example, drills that simulate defending against an overload situation can help players learn how to manage pressure and maintain their defensive shape. Practicing clearances, tackling, and intercepting passes can also improve the team’s ability to defend effectively under pressure.
Youth Soccer 4-3-3 Formation Attacking Drills
Attacking drills that are specific to the youth soccer 4-3-3 formation can significantly enhance the team’s ability to create and convert goal-scoring opportunities.
Overload Situations
Creating scenarios where the attackers outnumber the defenders is an effective way to practice breaking down a defense. This could involve 3v2 or 4v3 drills, where the focus is on quick passing, movement off the ball, and finishing. These drills help attackers learn how to take advantage of numerical superiority, making the most of their chances in front of the goal.
Crossing and Finishing
Crossing and finishing drills are essential for wingers and strikers. Coaches should design exercises where wingers deliver crosses into the box from different angles and distances, with the striker and midfielders practicing their timing and positioning to finish the crosses. This not only improves the quality of the crosses but also teaches attackers to anticipate and react to different types of deliveries.
Conclusion
The 4-3-3 formation is a powerful tool in youth soccer, offering a perfect balance between attack and defense. By mastering this formation, young players can develop a comprehensive understanding of the game and learn the importance of positioning, teamwork, and tactical discipline. Coaches who implement the 4-3-3 effectively can help their teams succeed on the field while also fostering the individual growth of their players.
Join our Upcoming Seasons and Camps to learn and practice youth soccer formations.
FAQs
What are the key positions in a 4-3-3 soccer formation?
The key positions in a 4-3-3 include four defenders, three midfielders (a holding midfielder and two central/attacking midfielders), and three forwards (a central striker and two wingers).
How do you coach a 4-3-3 formation in youth soccer?
Focus on teaching positional discipline, quick passing, and movement off the ball. Incorporate drills that simulate real-game scenarios to help players understand their roles within the formation.
What are the strengths of the 4-3-3 formation in youth soccer?
The 4-3-3 formation offers a balanced approach to attack and defense, promotes wide play through wingers, and allows for flexibility in both offensive and defensive transitions.
What are the common weaknesses of the 4-3-3 formation?
The 4-3-3 can be vulnerable to counter-attacks, especially if full-backs and midfielders are caught out of position, leaving gaps in the defense.
How do you defend against a 4-3-3 formation?
To defend against a 4-3-3, focus on maintaining a compact shape, applying pressure on the midfielders, and preventing wingers from exploiting space on the flanks.

Did you find this useful?


